
These instances are the result of the following procedure.
First there were files with random generated points in the plane on a
10,000,000 by 10,000,000 grid.
These points serve as terminals and were
converted to rectalinear graphs with L1 edge weights, by building the
Hanan grid (see Han66
).
Then these graphs were preprocessed with GeoSteiner a Software for computing Full-Steiner-Sets by M. Zachariasen and D.M. Warme . For a description of the Algorithm see War97 and WWZ00 .
The original point sets are from the OR-Library named ES10 to ES10000 corresponding to the number of points given.
Some results on solving the smaller instances without FST-preprocessing are published in KM98 . Since there seems to be no reason why today someone should try to solve these instances without FST-preprocessing anymore we only list the preprocessed ones.
Here is an picture of es250fst01 with solution: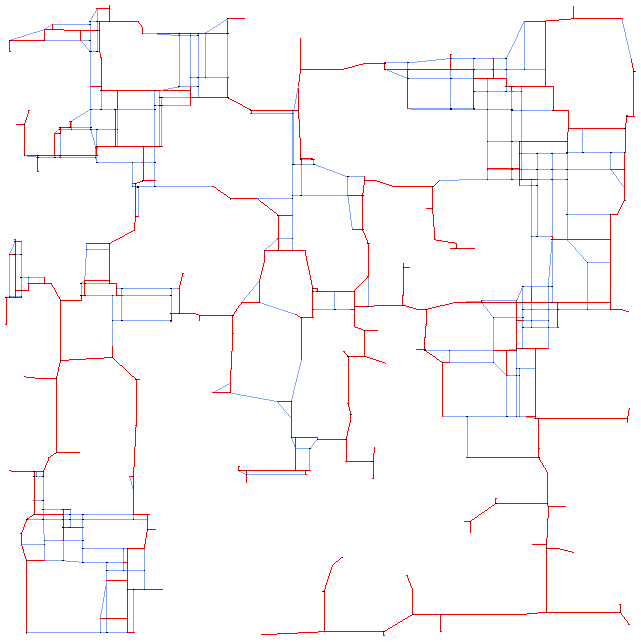
The files can be found in the download section.
| Name | |V| | |E| | |T| | DC | Opt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| es500fst01 | 1250 | 1763 | 500 | ?s | 162978810 |
| es500fst02 | 1408 | 2056 | 500 | ?s | 160756854 |
| es500fst03 | 1337 | 1933 | 500 | ?s | 162664661 |
| es500fst04 | 1296 | 1879 | 500 | ?s | 164110997 |
| es500fst05 | 1172 | 1627 | 500 | ?s | 160586161 |
| es500fst06 | 1335 | 1932 | 500 | ?s | 164685074 |
| es500fst07 | 1214 | 1700 | 500 | ?s | 160124233 |
| es500fst08 | 1349 | 1972 | 500 | ?s | 161248138 |
| es500fst09 | 1294 | 1853 | 500 | ?s | 162100435 |
| es500fst10 | 1203 | 1679 | 500 | ?s | 155581203 |
| es500fst11 | 1274 | 1808 | 500 | ?s | 161674316 |
| es500fst12 | 1322 | 1918 | 500 | ?s | 164009591 |
| es500fst13 | 1273 | 1814 | 500 | ?s | 161324201 |
| es500fst14 | 1477 | 2204 | 500 | ?s | 165984329 |
| es500fst15 | 1334 | 1927 | 500 | ?s | 160758467 |
The column DC classifies the difficulty of the instance.
The letter after class gives an impression how long it takes to solve the problem using state-of-the-art soft- and hardware. secounds means less than a minute (this includes instances which can be solved in fractions of a second). minutes means less than an hour. hours is less than a day and days is less than a week. weeks mean it takes really a long time to solve this instance. ? means the instance is not solved or the time is not known.
If the number in the Opt column is written in italics the optimum is not known. The number given is the best know upper bound.